We will show you how to easily convert content of your database tables into an XML file.
And all it takes is just a SQL statement and a CL command. We start off by preparing a sample table, this one will have three columns and three rows for testing:
CREATE TABLE qtemp.TESTXML (FIELD1 CHAR (10 ) , FIELD2 CHAR (256 ), FIELD3 NUMERIC (10 , 3));
INSERT INTO qtemp.TESTXML VALUES('Record1', 'Description1', 1);
INSERT INTO qtemp.TESTXML VALUES('Record2', 'Description2', 2);
INSERT INTO qtemp.TESTXML VALUES('Record3', 'Description3', 3);After executing the commands from above, our sample table has been created.
| Record1 | Description1 | 1.000 |
| Record2 | Description2 | 2.000 |
| Record3 | Description3 | 3.000 |
Additionally, we need a temporary table to store our XML data:
create table qtemp.myxml as (select xmlserialize(
xmlelement(NAME "MyXMLRecord", xmlelement(NAME "RecNbr", field3),
xmlelement(NAME "RecordName", trim(field1)),
xmlelement(NAME "RecordDescription", trim(field2)))
as char(1024)) as "XMLResult" from qtemp.testxml) with data;
As soon as this is done, our data has been stored within the table and we just have to export them into a text file in the IFS. You can do this by using the following CL command:
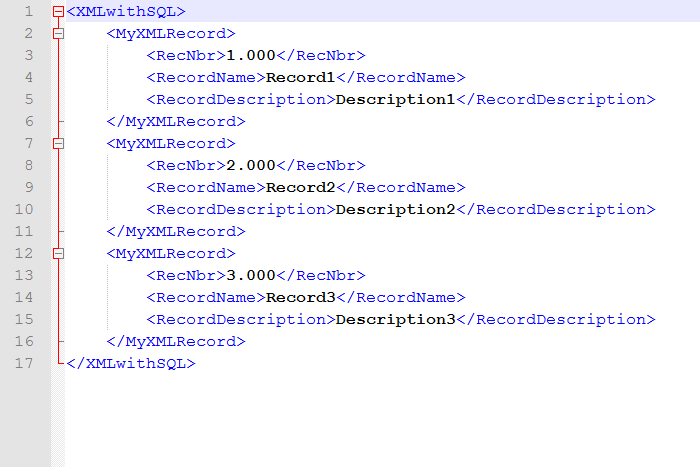
CPYTOIMPF FROMFILE(MYXML) TOSTMF('/myxml.xml') MBROPT(*REPLACE) FROMCCSID(1252) RCDDLM(*CRLF) STRDLM(*NONE)The final result will look like this:
<MyXMLRecord><RecNbr>1.000</RecNbr><RecordName>Record1</RecordName><RecordDescription>Description1</RecordDescription></MyXMLRecord> <MyXMLRecord><RecNbr>2.000</RecNbr><RecordName>Record2</RecordName><RecordDescription>Description2</RecordDescription></MyXMLRecord> <MyXMLRecord><RecNbr>3.000</RecNbr><RecordName>Record3</RecordName><RecordDescription>Description3</RecordDescription></MyXMLRecord>
Other structures within the XML can easily be created by using the respective keywords.